Event Logs in XP and Vista+
Presenter Notes
Event Logs
Contain a wealth of information about a system.
Windows monitors and logs several activities that occur within the OS.
- Amount makes it hard to determine what is occurring, though.
What Events to collect/care about?
- Account login
- account management
- application crashes
- system or service failures
- firewall events (Windows Firewall)
- event logs were cleared
- installation of new software/services
- device attachment
- pass the hash detection
Presenter Notes
Event Log Locations
Event logs are specific files on disk that get written to.
Readable by Event Viewer on a host machine.
Application
- Events occurring with an error, warning or information.
- Error is defined as a significant problem like loss of data or crash.
- Warning might indicate a problem.
- Information is a successful operation.
- Anti-Virus information
Security
- Audit events
- Logons
- Turned off by default on XP systems in HKLM/SECURITY/Policy/PolAdtEv
Presenter Notes
Setup
- Application setup.
- Windows update
System
- System events
- Services
- DNS Client
- Plug and play
Loads of different types of events and descriptions per event... Windows Security Logs
Presenter Notes
Windows XP
.EVT Files
Contains Application, System and Security logs
%systemroot%\system32\config
Services.exe contains event logs in process memory
Event Log Header and Event Record Strucutres used to represent logs.
def EVTLogHeader 0x30:
'HeaderSize'
'Magic' #LfLe
'OffsetOldest' #offset of oldest record
'OffsetNextToWrite' #offset of next record to be written
'NextID' #next event record ID
'OldestID' #oldest event record ID
'MaxSize' #maximum size of event record
'RetentionTime' #retention time of records
'RecordSize' #size of the record
Presenter Notes
def EVTRecordStruct 0x38:
'RecordLength' #Length of event log recorded
'Magic' #LfLe
'RecordNumber' #ID record within the event log
'TimeGenerated'
'TimeWritten'
'EventID' : #specific to event source and uniquely identifies the event
'EventType' #described above in EventTypes
'NumStrings' #strings to describe event.
Presenter Notes
Volatility Plugins
Requires knowing where the services.exe is located
1. Locate the services.exe binary in memory
[root&windows]#prof=WinXPSP3x86
[root&windows]#volatility -f sample004.bin --profile=$prof pslist | grep services
Volatility Foundation Volatility Framework 2.4
Offset(V) Name PID PPID Thds Hnds Sess Wow64
0x82146460 services.exe 672 624 15 238 0 0
2. Using vadinfo, find the location of an event log .
[root&windows]#volatility -f sample004.bin --profile=$prof vadinfo -p 672 | grep .Evt -B 9
VAD node @ 0x8226c2e0 Start 0x009b0000 End 0x009bffff Tag Vad
Flags: Protection: 4
Protection: PAGE_READWRITE
ControlArea @822a5008 Segment e15310d0
NumberOfSectionReferences: 1 NumberOfPfnReferences: 1
NumberOfMappedViews: 1 NumberOfUserReferences: 2
Control Flags: Accessed: 1, File: 1, HadUserReference: 1
FileObject @822a5f90, Name: \WINDOWS\system32\config\SecEvent.Evt
Presenter Notes
evtlogs
Performing manual parsing of the vad, while useful, is not needed as the Volatility authors wrote the evtlog plugin!
- Extracts and parses binary event logs from services.exe
- Files extracted from the VAD, much like we did in the previous slide.
- Handles corrupt events logs
- Can dump a raw log for external processing
- VERY slow
- Parsing through vad to find evt file
- Ensures evt file has proper header values
- parses evt
- LOTS of events on a system
Presenter Notes
evtlogs Usage
- --save-evt outputs .evt files and .txt files for parsing each log file.
- Can use evt files with external tools
- -D output/
[root&windows]#volatility -f sample004.bin --profile=$prof evtlogs -v --save-evt -D logs/ Saved raw .evt file to secevent.evt Parsed data sent to secevent.txt Saved raw .evt file to appevent.evt Parsed data sent to appevent.txt Saved raw .evt file to sysevent.evt Parsed data sent to sysevent.txt
Text is parsed as
Date\Time | Log Name | Computer Name | SID | Source | Event ID | Event Type | Message Strings
Presenter Notes
Tracing an Event
[root&windows]#ls logs/
appevent.evt appevent.txt secevent.evt secevent.txt sysevent.evt sysevent.txt
[root&windows]#cat logs/appevent.txt | grep -i warn
2012-03-28 16:18:28 UTC+0000|appevent.evt|RES-LAB01
|S-1-5-21-1417001333-1935655697-839522115-1003 (User: Jack)
|WinMgmt|63|Warning|HiPerfCooker_v1;Root\WMI
WinMgmt Event 63:
- A provider has not been registered in the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) namespace. Great risk is posed by these providers as the account in question is privileged and the provider may cause a security violation.
- TLDR; Provider is running as LocalSystem security!
HiPerfCooker_v1 is the instance name of _Win32Provider which registers information about physical WMI.
Lots of Googling shows this is not malicious, but could be an area of priv. esc if it contained a vulnerability.
Not every event log is a hint to an intrusion... use tools to parse, draw suspicions and validate! This event turned out to be nothing even though it was a warning.
Presenter Notes
Logging Policies
Security log turned off in XP by default.
Check registry settings to see what events are recorded to make analysis easier.
auditpol
Prints out the Audit Policies from HKLM\SECURITY\Policy\PolAdtEv
[root&windows]#cat logs/secevent.txt
[root&windows]#
No logs.. should expect all events to be non-logging.
[root&windows]#volatility -f sample004.bin --profile=$prof auditpol
Auditing is Disabled
Audit System Events: Not Logged
Audit Logon Events: Not Logged
Audit Object Access: Not Logged
Audit Privilege Use: Not Logged
Audit Process Tracking: Not Logged
Audit Policy Change: Not Logged
Audit Account Management: Not Logged
Audit Dir Service Access: Not Logged
Audit Account Logon Events: Not Logged
Presenter Notes
Auditpol with security events logged
[root&windows]#volatility -f winXpLogs.bin --profile=$prof auditpol
Auditing is Enabled
Audit System Events: S/F
Audit Logon Events: Not Logged
Audit Object Access: S/F
Audit Privilege Use: S
---CUT---
S = successful operations logged
F = failed operations are logged
Presenter Notes
Windows Vista+
Logs are now in XML binary format
Event log extension is now ".Evtx"
More logs than on XP... more than 60 in %systemroot%\system32\winevt\Logs - My machine has 131
Description of strings are contained within the event logs!
Presenter Notes
Event Log ID in Vista+
VistaEventId = PreVistaEventId + 4096
Micro$oft did this as the event content changed and they wanted to preserve legacy support.
Event for logon = 528 on PreVista PostVista eventID = 4624
4624 = 528 + 4096
Presenter Notes
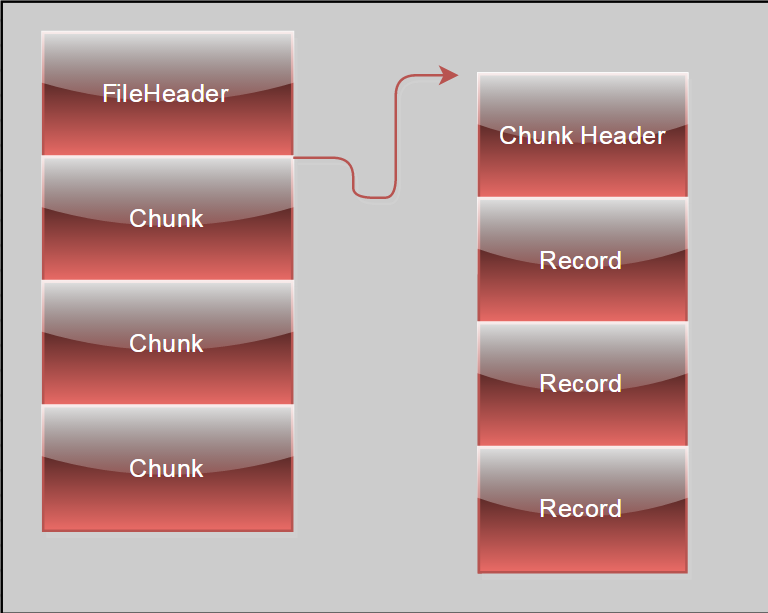
Evtx Format
FileHeader
Basic information about the log file
Contains the number of chunks present in a file
Flags
1 = Full. Maximum configuration size and new records might not be written.
0 = Dirty. The log was opened and change.
Chunk (Current Chunk mapped into memory, Not all chunks have to be)
Contains XML templates and a series of event records
Event Records
XML
Messages
Timestamp
Record length
Event ID
Presenter Notes
Layout of Evtx file
Presenter Notes
Headers of Evtx
def FileHeader:
Magic = "ElfFile"
No. of current chunk
No. of next record
Header space used,
Minor version, constant 1
Major version, constant 3
Size of header, constant 4096
Chunk count
Flags (0 = dirty log, 1 = full log)
Check sum
def Chunk:
Magic = "ElfChnk"
Number of first record in log
Number of last record in log
Number of first record in file
Number of last record in file
Size of header
Offset of last record
Offset of next record
Check sum
def EventRecord:
Magic = 0x2a 0x2a 0x00 0x00
Record Length
EventID
TimeCreated
Event messages, binary XML
Length
Presenter Notes
Binary XML schema
def XMLschema:
<Events>
<Event>
<System>
<EventID>1</EventID>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2006-10-08T09:21:28.415Z"/>
<EventRecordID>573</EventRecordID>
</System>
<EventData>
</EventData>
</Event>
</Events>
Presenter Notes
Volatility with Evtx
Volatility cannot parse Evtx files in memory.
Extract the logs from memory and parse them with an external tool.
Only extract logs you think you might need
- Security never a bad idea...
Python-evtx is easy and in python!
- Developed by Willi Ballenthin at Mandiant. (He has a ton of other python scripts to do IR!)
- Install through pip or clone the github repo and run setup.py
Presenter Notes
Dumpfiles
Files kept in memory cache can be recovered with this plugin.
Files may not be completely mapped in memory and missing sections are padded with 0's.
Iterates through the VAD and extracts files with DataSectionObject, ImageSectionObject or SharedCacheMap mappings.
Usage
-r REGEX dumps all files matching
-i ignore case in REGEX
-o physical offset (Useful for processes not in PsActiveProcess or that have no PID)
-D dump dir
-S summary file
-p PID
-n dump by original file name
default files are dumped in the form of file.[PID].[OFFSET].[EXT]
File EXT
- img – ImageSectionObject
- dat - DataSectionObject
- vacb – SharedCacheMap
Presenter Notes
Dumpfiles in Practice
[root&windows]#prof=Win7SP0x86
[root&windows]#file=sample002.bin
[root&windows]#volatility -f $file --profile=$prof dumpfiles --regex .evtx$ -i -D eventsW7/
[root&windows]#cd eventsW7/
[root&eventsW7]#evtxinfo file.748.0x8430d008.vacb
Information from file header:
Format version : 3.1
Flags : 0x00000001
File is : dirty
Log is full : no
Current chunk : 0 of 1
Oldest chunk : 1
Next record# : 4
Check sum : pass
Suspected updated header values (header is dirty):
Current chunk : 1 of 1
Next record# : 4
Information from chunks:
Chunk file (first/last) log (first/last) Header Data
- ----- --------------------- --------------------- ------ ------
* 1 1 3 1 3 pass pass
2 [EMPTY]
3 [EMPTY]
[root&eventsW7]#evtxdump file.748.0x8430d008.vacb
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" standalone="yes" ?>
<Events>
<Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event"><System><Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-CodeIntegrity" Guid="4ee76bd8-3cf4-44a0-a0ac-3937643e37a3"></Provider>
<EventID Qualifiers="">3024</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>3</Level>
<Task>10</Task>
<Opcode>109</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8000000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2012-07-06 07:33:38.591425"></TimeCreated>
<EventRecordID>1</EventRecordID>
<Correlation ActivityID="" RelatedActivityID=""></Correlation>
<Execution ProcessID="4" ThreadID="48"></Execution>
<Channel>Microsoft-Windows-CodeIntegrity/Operational</Channel>
<Computer>WIN-N3QCH29P1O5</Computer>
<Security UserID="S-1-5-18"></Security>
</System>
<EventData><Data Name="Status">0xc0000034</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Presenter Notes
Log Wiping
Attackers can be smart and erase all of the log files on disk using the Windows API.
- MetaSploit implements this in the meterpreter shell
BOOL ClearEventLog(
HANDLE hEventLog, // handle to event log from advapi32.OpenEventLog()
LPCTSTR lpBackupFileName // name of backup file. Can be NULL.
);
Easy to produce.
Need to specify each log to erase... attacks can forget a few!
Security log commonly erased.
Because event logs are cached in memory or are still resident, some logs can be recovered!
Important Note
- An event is triggered when an event log is cleared to the security log.
Presenter Notes
Happy
$ for b in $(git fsck --lost-found | grep blob | awk '{print $3}');
do git cat-file -p $b > ../$b ; done
Resolve git conflicts before checking out a branch... thanks to the inetnet (other people did this, too), I did not lose all of this presentation! :)
